Will the U.S. Retake Bagram Air Base? Why It Matters and What’s at Risk
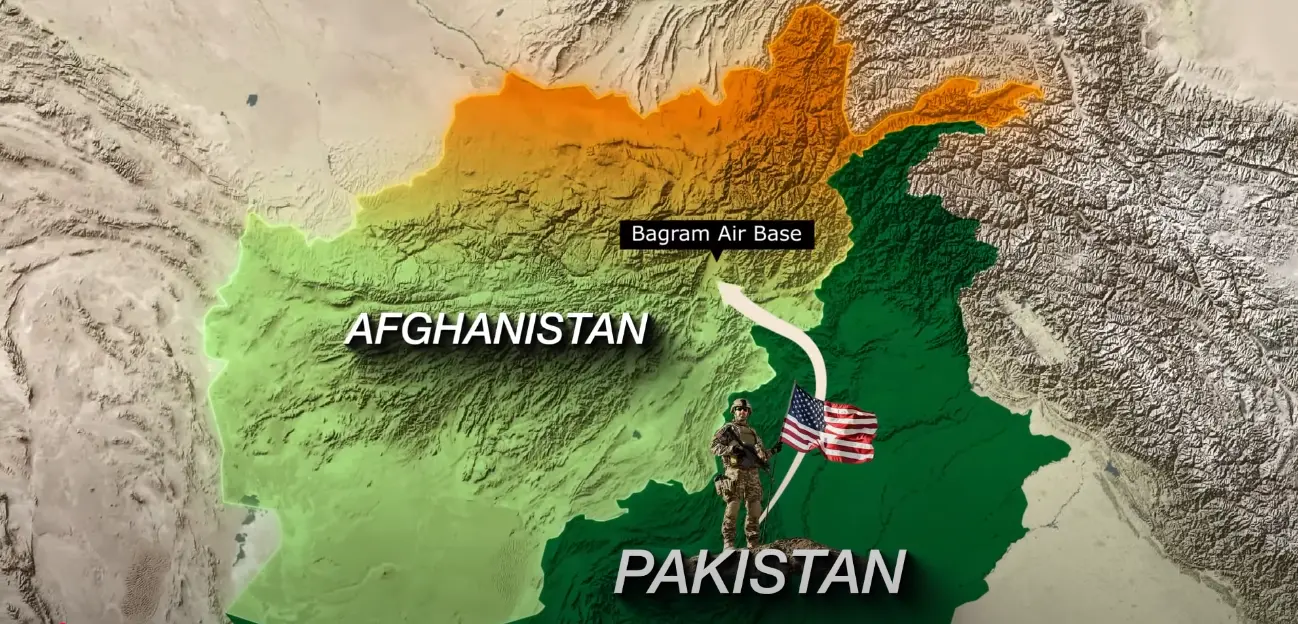
When Donald Trump recently said the U.S. wants control back of Bagram Air Base in Afghanistan, it caught many off guard. The base was abandoned in 2021 as US troops withdrew, and the Taliban now control it. Trump claims Bagram is “an hour away from where China makes its nuclear weapons,” making its location particularly strategic. But with Afghanistan pushing back and major powers weighing in, this is no simple return. Let’s dig into what’s on the table, what supporters see vs critics warn, and what this could mean.
What Trump Is Saying & What’s Already Public
- Statement of Intent: During a press conference with UK PM Keir Starmer, Trump explicitly said the U.S. is trying to “get Bagram back.” He cited its proximity to China and said abandoning it was a mistake.
- Location & Background: Bagram is in Parwan Province, about 44 km north of Kabul. Before the withdrawal, it was one of the largest U.S. military bases in Afghanistan.
- Strategic Rationale: Besides “monitoring China,” the U.S. reportedly sees Bagram as helpful for counterterrorism operations, regional presence, and perhaps influence in Central Asia.
Afghanistan & China’s Reactions
- Taliban Response: Taliban officials have firmly rejected the idea of any renewed U.S. military presence in Afghanistan. They argue Afghanistan’s sovereignty must be respected and foreign troops should not return.
- China’s Position: Beijing has also urged that any decisions around Bagram must respect Afghanistan’s independence, warning against moves that could destabilise the region.
Supporters’ Arguments: Why Some Believe Reclaiming Bagram Makes Sense
- Strategic Depth against China
Supporters argue the U.S. needs a base in Afghanistan to counterbalance China’s influence, especially in regions close to the Chinese border. Bagram’s proximity gives air and intelligence gain.
- Counterterrorism & Regional Security
With threats from ISIS, local militant groups, and extremist networks, having a strategic hub could help the U.S. monitor, respond, and gather intelligence more efficiently.
- Political Messaging
Reclaiming Bagram can be presented domestically as reclaiming what was lost — strengthening U.S. geopolitical posture. Also, a signal to allies and rivals that the U.S. is reasserting its presence where it believes strategic interests are under threat.
Critics’ View: Risks, Challenges & Questions
- Sovereignty & Legitimacy Concerns
The Taliban and many Afghans see any return of U.S. troops as a violation of sovereignty. The Doha agreement and subsequent understandings emphasised foreign military non-presence. Reintroducing military presence could undermine political relationships and trust.
- Logistical & Operational Challenges
Retaking Bagram would likely require major military effort, approvals, security guarantees, and infrastructure assessments. It’s not just “landing in and occupying” — Taliban control, local sentiment, and on-ground risk make any military move complex. Experts warn it could resemble a full re-invasion.
- International Pushback & Diplomatic Fallout
China has already called for restraint and respect for Afghan sovereignty. Other regional players may view a U.S. military return as destabilising, potentially sparking tension. Also, such a move might be opposed by international law experts and nations wary of foreign military presence.
- Public Messaging vs Reality
Some of Trump’s statements remain vague: how many troops, under what mandate, under which agreements with the Taliban, etc. The claim about “China makes nuclear weapons near there” is controversial and not clearly verified in open sources. Some critics argue this may be rhetoric rather than policy fully worked-out out.
What Could Happen / What India & Others Might Need to Watch
- Diplomatic Engagement: The U.S. might attempt to negotiate with the Taliban for access rather than overt military reoccupation.
- Afghan Legal & Political Framework: Any agreement would likely require terms that address sovereignty, duration, oversight, and local consent.
- Regional Alliances & Reactions: Pakistan, China, Iran, and Central Asian countries will watch closely. Their interests and responses will matter.
- Signal to China: Even if no immediate base takeover happens, the talk itself is a strategic message.
Conclusion
Trump’s renewed push to reclaim Bagram Air Base marks a major flashpoint in global geopolitics. For supporters, regaining it is about strategy, deterrence, and regional posture. For critics, the concerns about sovereignty, operational risk, and diplomatic fallout are substantial. The truth likely lies between the two extremes: reclaiming Bagram would not be simple or risk-free, but neither is the status quo undefendable.
Track official statements from the U.S., Afghanistan (Taliban), and China; monitor whether negotiations occur; observe local Afghan reactions. Those will signal whether Bagram becomes a flashpoint or remains an ambition.
Disclaimer: This article is based on publicly available reports and independent analysis. Readers are encouraged to consult multiple sources for a complete picture. Source - Reuters, India Today




No comments yet. Be the first to comment!