Trump says about Afghanistan Bagram Airbase: BAD THINGS ARE GOING TO HAPPEN!

Over the past few days, reports have suggested that the United States may consider re-entering Afghanistan, specifically targeting Bagram Airbase—the largest U.S. base during its two-decade presence. Trump has issued a direct warning: “Bad things will happen if Afghanistan does not return Bagram Airbase.” This statement has raised questions about the strategic, military, and geopolitical motivations behind a potential U.S. return. Understanding the facts can help assess possible regional and global implications.
Historical Context of Bagram Airbase
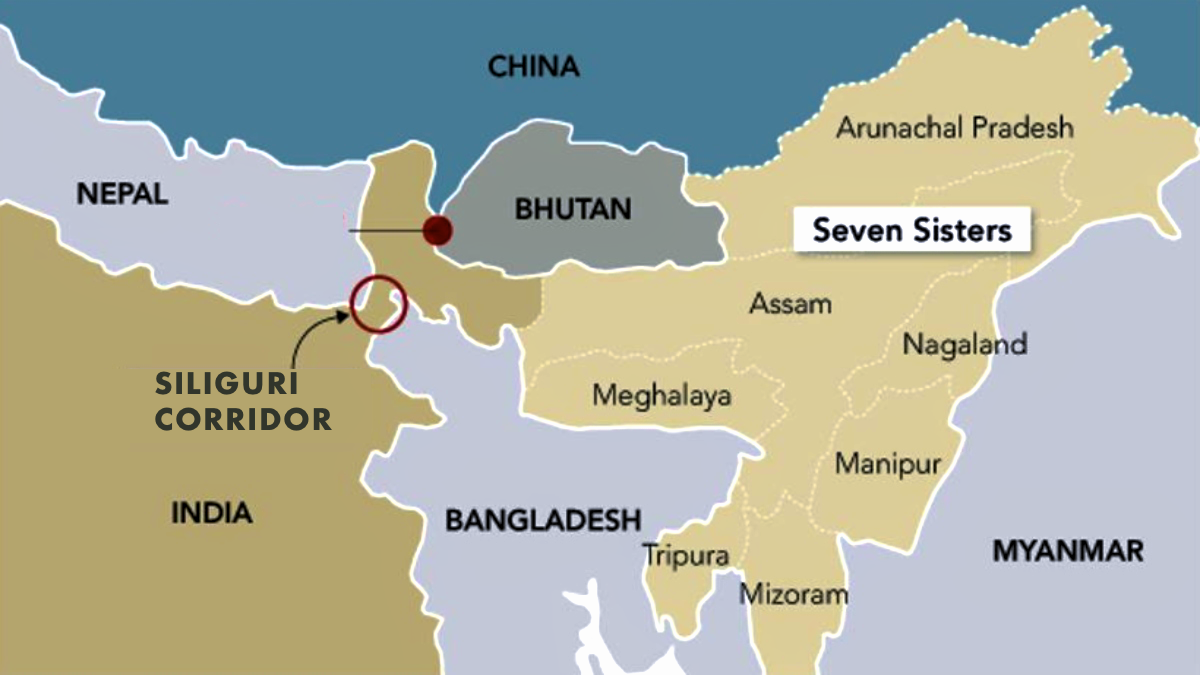
Bagram Airbase is located in Parwan Province, just north of Kabul. From 2001 to 2021, it served as the largest U.S. military base in Afghanistan, acting as:
- A logistics hub with a long runway for heavy-lift aircraft.
- A centre for intelligence, detention, and command operations.
- A fortified site surrounded by mountains for strategic defence.
Trump’s reference to “building” the base during U.S. operations suggests he views it as a legitimate strategic asset.
Strategic Importance
- Proximity to China: Bagram is relatively close to the Chinese border via the Wakhan Corridor, giving the U.S. a potential platform to monitor or counter Chinese influence in the region.
- Counter-Terrorism: Afghanistan still hosts extremist groups, including remnants of ISIS and al-Qaeda. A U.S. presence could provide a base for counter-terrorism operations.
- Regional Leverage: Control of Bagram offers strategic influence over neighbouring countries such as Pakistan, Iran, and Central Asian states.
Analysts suggest that Bagram could serve as a hub for projecting U.S. power across South and Central Asia.
Possible U.S. Actions
- Military Operations: Securing Bagram would likely require large-scale combat operations to bypass Taliban defences.
- Force Deployment: Thousands of troops, along with air defence and logistical support, would be needed to fortify the base against local threats.
- Infrastructure Restoration: Rebuilding command centres, medical facilities, supply depots, and other essential infrastructure would be necessary for long-term operations.
Constraints and Challenges
- Sovereignty and International Law: Afghanistan is under Taliban control. Any unilateral U.S. action would likely violate international norms, creating diplomatic and legal challenges.
- Logistics and Airspace Access: The U.S. would need permission to use regional airspace or rely on neighbouring countries like Pakistan or Central Asian states, complicating operations.
- Regional Opposition: Pakistan, Russia, and Iran are expected to oppose U.S. intervention. Pakistan, in particular, faces security concerns and potential domestic backlash.
Non-Military Options
Before a full-scale intervention, the U.S. could explore:
- Diplomatic Pressure: Isolating the Taliban politically or economically.
- Sanctions: Targeting Taliban-linked individuals or financial networks.
- Covert Operations: Intelligence missions, cyber-attacks, or limited airstrikes near strategic locations.
Taliban’s Position
Taliban officials have dismissed Trump’s statements, asserting that Bagram will remain under Afghan control. They indicate that the U.S. cannot regain the base without confronting local resistance and complex regional dynamics.
Regional Implications
- China: Likely to view U.S. activity near its border as strategic encirclement.
- Pakistan: Concerned about its role if the U.S. re-enters Afghanistan.
- Russia and Iran are expected to oppose U.S. moves, complicating the regional security environment.
Any U.S. action in Bagram would influence regional security, diplomacy, and military postures across South and Central Asia.
Conclusion
Trump’s warning regarding Bagram Airbase highlights U.S. strategic interest in Afghanistan, but significant political, logistical, and legal constraints exist. While military, diplomatic, and covert options are possible, regional opposition and international law complicate any potential action. Observing these developments is essential for understanding broader U.S. strategy and regional geopolitical shifts.
Disclaimer: This article is based on publicly available reports and independent analysis. Readers are encouraged to consult multiple sources for a complete picture.




No comments yet. Be the first to comment!